DATA CABLING
Data Cabling is a method of connecting multiple devices e.g PC’s, Printers, CCTV cameras, servers within an IT network. There are essentially two types of data cable, copper and fibre, within these two types of cable there are different grades which ultimately result in different standards.
Cables are ran to a floor box or wall mounted point close to where the device will be situated, it will be ran from a central location where a communication cabinet will be installed, in most cases all cables go back to the same cabinet but for a large scale deployment you could have a cabinet per floor. Fibre cables can be ran much longer distances than copper, for this reason fibre normally connects multiple cabinets together while copper cables connect individual devices and will go back to the closest cabinet.


Network Cabling
Network cables are used to connect and transfer data and information between computers, routers, switches and storage area networks . These cables are essentially the carrier or media through which data flows.
There are different types of communications cables, and the appropriate type to use will depend on the structure of the system. The most commonly used types of communications cables are dominated by what is referred to as “twisted pair cable”. In local area networks; typically office environments, retail and commmercial sites, copper commincations cabling, i.e.,twisted pair cable is by far the most commonly used type of cable.
Fibre Optic Cabling
A fiber optic cable is a network cable that contains strands of glass fibers inside an insulated casing. They're designed for long-distance, high-performance data networking, and telecommunications. Compared to wired cables, fiber optic cables provide higher bandwidth and transmit data over longer distances. Fiber optic cables support much of the world's internet, cable television, and telephone systems.
Why use optic fibre cable?
- They have practically unlimited information
- They have high carrying capacity (very broad bandwidth, THz or Tbits/s)
- They have very low transmission losses
- They do not dissipate heat
- They are immune to cross-talk and electromagnetic interference
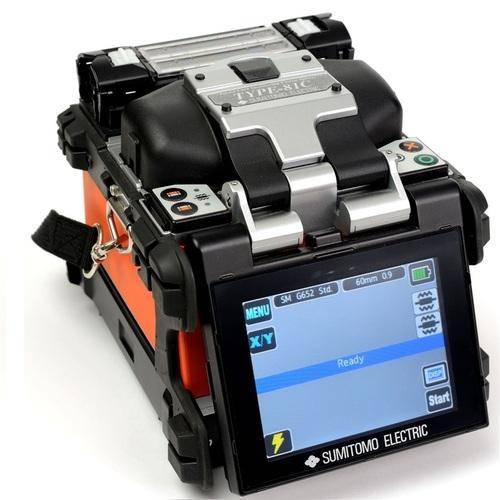


Fibre Splicing
Fiber optic splicing is an important method of joining two fiber optic cables together. It is a preferred solution when an available fiber optic cable is not sufficiently long enough for the required distance. Splicing is also designed to restore fiber optic cables when they are accidentally broken. Nowadays, fiber optic splicing is widely deployed in telecommunications, LAN (Local Area Network) and networking projects. Typically, fiber optic splices can be undertaken in twistedo ways: fusion splices and mechanical splices.
Fusion Splicing Methods -Fusion splicing is a permanent connection of two or more optical fibers by welding them together using an electronic arc. It is the most widely used method of splicing as it provides for the lowest loss, less reflectance, strongest and most reliable joint between two fibers. When adopting this method, fusion splicing machines are often used. Generally, there are four basic steps in fusion splicing process: